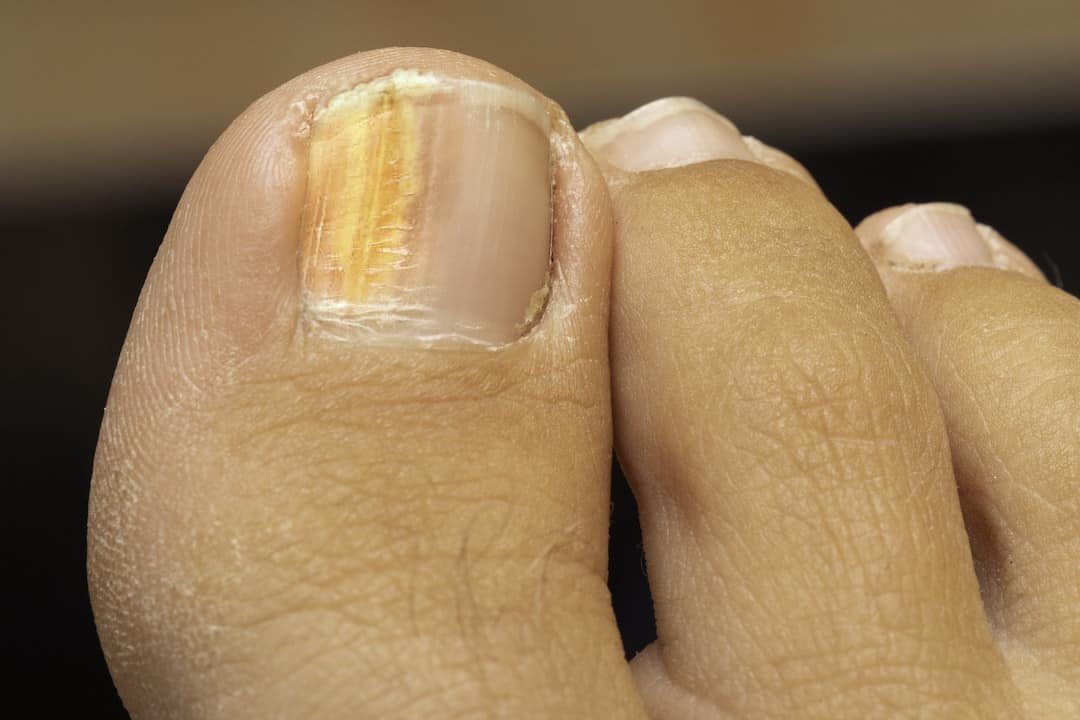
Nail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, is a common condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. If you’re dealing with toenail fungus, you may have noticed changes in your nails over time. But what do these changes mean? Is your toenail fungus dying, or is it simply undergoing transformations? In this expert’s guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, treatments, and prevention strategies for nail fungus to help you understand the nuances of this condition.
Introduction: The Importance of Discussing Nail Fungus
Nail fungus is a prevalent issue that impacts a significant portion of the population. In fact, studies estimate that approximately 10% of adults experience nail fungus at some point in their lives. Nail fungus is more than just a cosmetic concern; it can cause discomfort, pain, and affect your overall well-being.
Understanding the changes that occur during the course of nail fungus is crucial for managing the condition effectively. By shedding light on the causes, symptoms, available treatments, and prevention strategies, we aim to provide you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about your nail health.
Causes of Nail Fungus
Nail fungus is primarily caused by fungal organisms called dermatophytes. These microscopic organisms thrive in warm and moist environments, making the feet an ideal breeding ground. However, several factors can contribute to the development of nail fungus, including:
- Exposure to damp environments: Frequent exposure to damp areas, such as public pools, locker rooms, or sweaty shoes, increases the risk of developing nail fungus.
- Trauma to the nail: Injuries to the nail, such as cracks, cuts, or nail separation, can create entry points for fungal infection.
- Weakened immune system: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with diabetes or HIV/AIDS, are more susceptible to nail fungus.
- Age: The risk of nail fungus increases with age as nails become more brittle and prone to damage.
- Poor circulation: Conditions that affect blood circulation, such as peripheral artery disease, can contribute to the development of nail fungus.
Understanding the causes of nail fungus can help you take preventive measures to minimize the risk of infection.
Symptoms and Impact on Daily Life
Nail fungus can present with a variety of symptoms that can impact your daily life. Initially, you may notice subtle changes in the affected nails, which can progress over time. Common symptoms of nail fungus include:
- Discoloration: Infected nails may appear yellow, brown, or have white spots. The color change is often a result of fungal activity underneath the nail.
- Thickening: As the infection progresses, the nail may thicken, becoming more difficult to trim and prone to crumbling.
- Brittleness: Infected nails can become brittle, leading to nail breakage or splitting.
- Distorted shape: The shape of the nail may change, becoming irregular or deformed.
- Foul odor: In some cases, nail fungus can cause a foul smell emanating from the affected nails.
These symptoms can impact your daily life by causing discomfort, pain, and embarrassment. Engaging in activities such as walking, exercising, or wearing certain types of shoes may become challenging.
Nail fungus can also spread to other nails or to other individuals through direct contact. It’s important to take precautions and seek treatment to prevent the spread of infection. Treating nail fungus can be a lengthy process, often taking several months to a year to fully resolve.
Treatment Options for Nail Fungus
When it comes to treating nail fungus, several options are available. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the infection, your overall
health, and personal preferences. Here are the most common treatment options for nail fungus:
1. Over-the-Counter Medications
Over-the-counter antifungal creams, ointments, and nail lacquers are readily available for mild to moderate cases of nail fungus. These products often contain ingredients like clotrimazole or terbinafine, which work by inhibiting the growth of fungal organisms. It’s important to use these medications as directed and continue treatment for the recommended duration.
2. Prescription Medications
For more severe or persistent cases of nail fungus, prescription medications may be necessary. Oral antifungal medications, such as terbinafine or itraconazole, are commonly prescribed. These medications work systemically to eliminate the fungal infection. However, they may have potential side effects and require periodic blood tests to monitor liver function. Prescription medications are usually taken for several weeks or months, depending on the severity of the infection.
3. Nail Removal
In certain cases where the infection is severe or does not respond to other treatments, surgical nail removal may be recommended. This procedure involves removing the infected nail to allow for the growth of a healthy nail.
4. Laser Therapy
Laser therapy is a relatively new treatment option for nail fungus. It involves using laser energy to target and destroy the fungal infection. While this method shows promise, more research is needed to determine its long-term effectiveness.
5. Natural Remedies
Some individuals may opt for natural remedies to complement conventional treatments. Natural remedies such as tea tree oil, vinegar soaks, or essential oils have been suggested to have antifungal properties. However, their effectiveness may vary, and it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before using them.
It’s worth noting that the effectiveness of treatment can vary from person to person. Nail fungus is a stubborn condition, and recurrence is possible even after successful treatment. Consistency, patience, and following the recommended treatment plan are essential for optimal results.
Practical Tips to Prevent Nail Fungus
Prevention is key when it comes to nail fungus. Here are some practical tips to help you minimize the risk of developing this condition:
- Practice good foot hygiene: Wash your feet regularly with soap and water, making sure to dry them thoroughly, especially between the toes.
- Keep your feet dry: Avoid prolonged exposure to damp or sweaty environments. If your feet tend to sweat, consider using antifungal foot powders or wearing moisture-wicking socks.
- Protect your feet in public areas: Wear sandals or shower shoes in public showers, locker rooms, and pool areas to reduce the risk of fungal exposure.
- Choose breathable footwear: Opt for shoes made of breathable materials, such as leather or mesh, to allow proper ventilation and reduce moisture buildup.
- Trim your nails properly: Cut your nails straight across and avoid cutting them too short. This can help prevent nail trauma and reduce the risk of fungal infection.
- Avoid sharing personal items: Do not share nail clippers, files, or footwear with others, as this can increase the risk of spreading fungal infections.
By incorporating these preventive measures into your daily routine, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing nail fungus.
Conclusion
Nail fungus is a common condition that can impact your nail health and overall well-being. Understanding the causes, symptoms, available treatments, and prevention strategies is essential for effectively managing nail fungus. While nail fungus can be stubborn, it is treatable. By seeking timely treatment, following preventive measures, and practicing good foot hygiene, you can maintain healthy nails and minimize the impact of nail fungus on your daily life. If you’re experiencing nail fungus symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.